Not actual patient.
Not actual patient.
LET’S TALK ABOUT
PATIENTS LIKE SARAH
A patient with type 1 diabetes struggling to maintain glycemic control
On basal insulin and injects insulin aspart before meals
Has an A1C of 8.2 and is concerned about hypoglycemia
Tired of scheduling meals around injections
Anxious about frequency of continuous glucose monitor (CGM) alerts
Makes Sarah
realize she’s not
maintaining control
GIVE PATIENTS LIKE SARAH IMPROVED MEALTIME CONTROL WITH AFREZZA® 1,2,7
- Afrezza delivers an ultra-rapid insulin response with absorption in the blood in <1 minute1,4
- Time to first measurable effect is ~12 minutes1
- Patients inhale Afrezza at mealtime, when they are ready to eat, with no needlesticks1
- Afrezza was proven to be non-inferior to subcutanous (SC) rapid-acting insulin in
clinical trials1,7
 Not actual patient.
Not actual patient.
Patient Profile:Sarah
Drag & Drop:What features of an inhaled insulin might help a patient like Sarah?
Drag the items to sort them in the order of importance to you, with 1 being the most important

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S TALK ABOUT
MEALTIME CONTROL
Afrezza® delivers a rapid insulin response for significant improvements in mealtime glycemic control2
POSTPRANDIAL GLUCOSE (PPG) LEVELS OVER 4 HOURS VS SC RAPID-ACTING COMPARATOR2
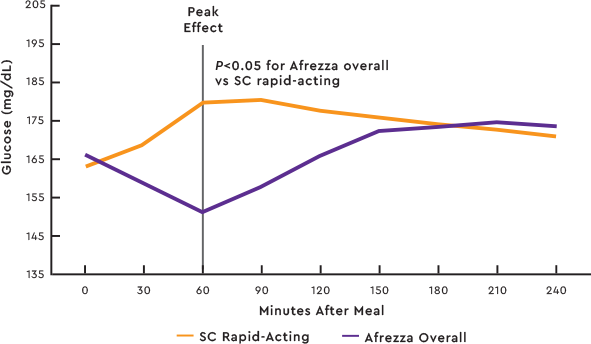

Study design:Afrezza efficacy was studied in a pilot, investigator-led, open label, multicenter trial of 60 patients with t1dm with A1C levels ≥6.5% and ≤10%. Individuals were randomized to treatment with Afrezza (n=26) or subcutaneous (SC) rapid-acting insulin (n=34). All were required to wear a real-time CGM throughout the trial.2

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S TALK ABOUT
MEALTIME CONTROL
Afrezza® delivers a rapid insulin response for significant improvements in mealtime glycemic control2
PPG EXCURSIONS 1-4 HOURS AFTER MEAL VS SC RAPID-ACTING COMPETITOR2
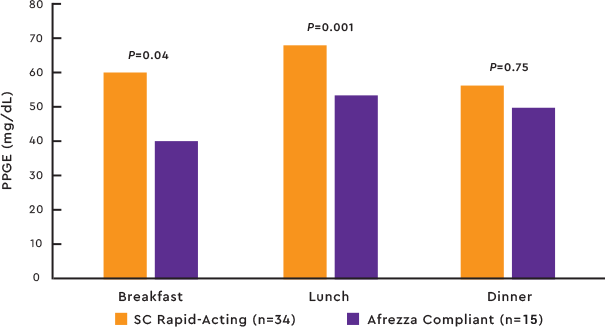

Study design:Afrezza efficacy was studied in a pilot, investigator-led, open label, multicenter trial of 60 patients with t1dm with A1C levels ≥6.5% and ≤10%. Individuals were randomized to treatment with Afrezza (n=26) or subcutaneous (SC) rapid-acting insulin (n=34). All were required to wear a real-time CGM throughout the trial.2

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S TALK ABOUT
THE SAFETY PROFILE
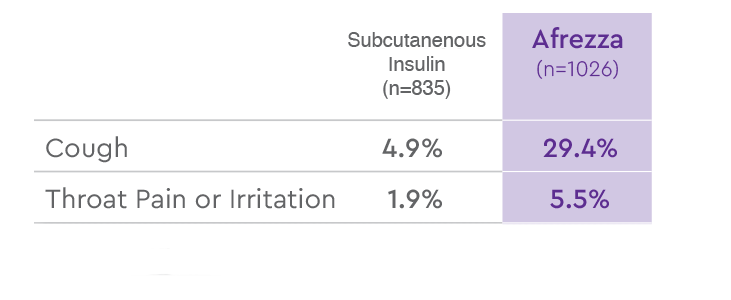
Afrezza® has been studied in over 3,000 patients with diabetes1
MOST COMMON ADVERSE REACTIONS (ARs) IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES,
EXCLUDING HYPOGLYCEMIA1

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S CHANGE THE CONVERSATION BY
CONSIDERING THE PATIENT
TOTAL HYPOGLYCEMIA AS A FUNCTION OF TIME IN THE TYPE 1 STUDY7
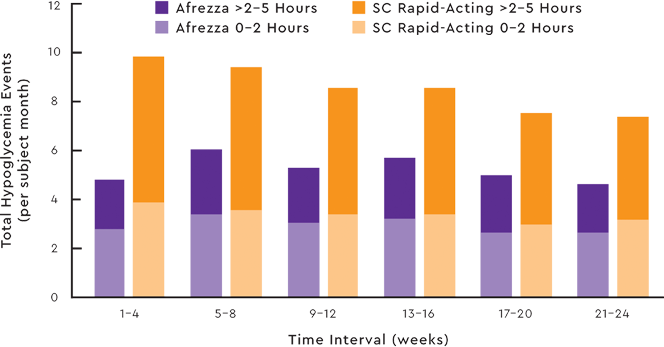
Study design:This open-label non-inferiority trial compared the change in A1C from baseline to week 24 of prandial Afrezza (n=174) with that of SC rapid-acting insulin (n=170), both with basal insulin,
in adult patients (≥18 years) with type 1 diabetes and A1C of 7.5% to 10%.
Afrezza provided less A1C reduction than SC rapid-acting insulin,
and the difference was statistically significant. More subjects in the SC rapid-acting insulin group achieved the A1C target of ≤7%.7

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S CHANGE THE CONVERSATION WITH
PROVEN CONTROL
Switching to Afrezza® maintained acceptable glucose control1,7
MEAN A1C LEVELS OVER 24-WEEK TREATMENT PERIOD1,7
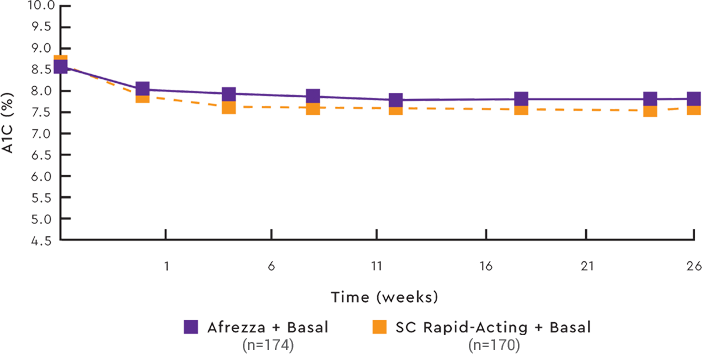

Data from an open-label non-inferiority trial compared the change in A1C from baseline to week 24 of prandial Afrezza (n=174) with that of SC rapid-acting insulin (n=170), both with basal insulin, in adult patients (≥18 years) with type 1 diabetes and A1C of 7.5% to 10%. Afrezza provided less A1C reduction than rapid-acting insulin, and the difference was statistically significant. More subjects in the SC rapid-acting group achieved the A1C target of ≤7%.7

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S CHANGE THE CONVERSATION WITH
PROVEN CONTROL
Switching to Afrezza® delivered significantly more time-in-range2
MEALTIME SUPPLEMENT AT
1 AND/OR 2 HOURS POST-MEAL2

TIME-IN-RANGE (TIR)2
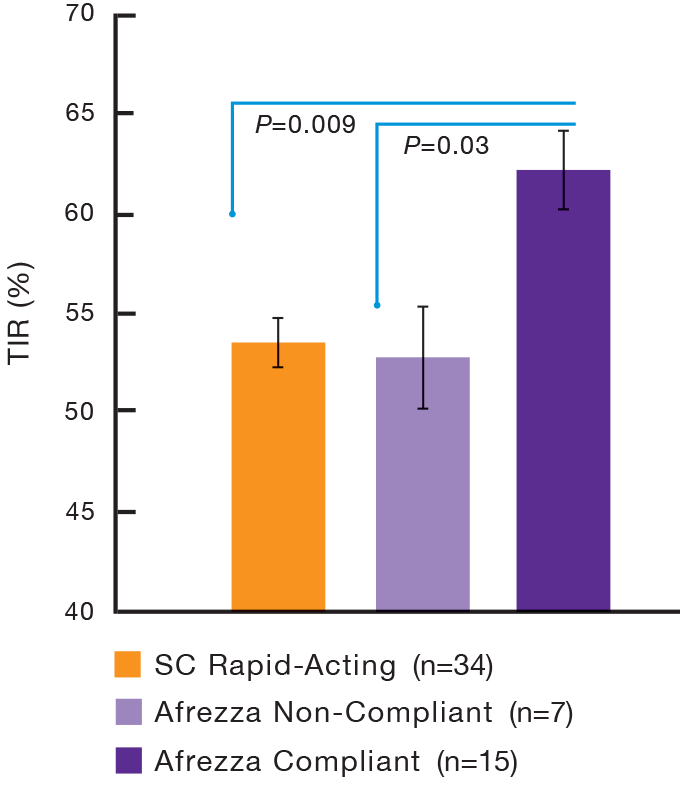

Data from a pilot, investigator-led, open-label, multicenter trial of 60 patients with t1dm with A1C levels ≥6.5% and ≤10%. Individuals were randomized to treatment with titrated Afrezza (n=26) or titrated SC rapid-acting insulin (n=34). All were required to wear a real-time CGM throughout the trial.2

Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S CHANGE THE CONVERSATION ABOUT
DOSING + TITRATION
Afrezza® mealtime control is possible with flexible dosing1
4, 8 & 12 Units
Available Afrezza cartridge options1
1.5x
Conversation from injectable insulin to Afrezza units for comfortable effect7,8,9
Adjust Dosing
As needed to achieve optimal control1
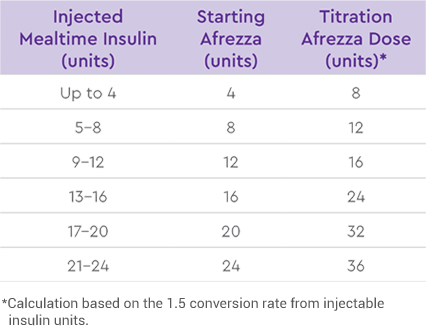
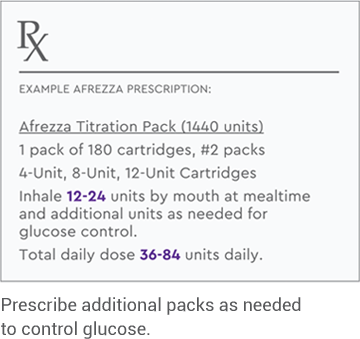
This Afrezza Titration Pack offers flexibility for patients getting started:


Sarah’s
Journey
ranking
LET’S CHANGE THE CONVERSATION ABOUT
DOSING + TITRATION
Afrezza® mealtime control is possible with flexible dosing1
INITIAL INSULIN DOSE
CONVERSION + TITRATION DOSE1